Amazing stuff! Could this be a breakthrough?
"A sulfurous intermediate could be the missing puzzle piece that explains how simple molecules on early Earth first assembled into proteins. New research shows that aminoacyl–thiols can react with RNA molecules to initiate the first steps of protein synthesis, while avoiding competing side reactions, all without the need for enzymes. ...
In particular, the initial activating step – an aminoacylation reaction – has proven challenging to replicate without enzymes. Previous studies have proposed various electrophiles including phosphates, imidazoles, and N-carboxyanhydrides as chemical activating agents but the resulting species are highly reactive, leading to uncontrolled background reactions and poor stability in water.
According to ... [a team] ... the solution must therefore involve a milder mechanism of activation. The researchers chose to focus their attention on thioesters, which are prevalent motifs in metabolic processes. Through a panel of experiments, they demonstrated that aminoacyl–thiols derived from from prebiotic precursors provided sufficient activation to enable these units to selectively bind to tRNA molecules. The water-based reaction seamlessly tolerated 15 different amino acid units while also suppressing the uncontrolled competing reactions of these amino acids directly with each other. ..."
From the abstract:
"To orchestrate ribosomal peptide synthesis, transfer RNAs (tRNAs) must be aminoacylated, with activated amino acids, at their 2′,3′-diol moiety, and so the selective aminoacylation of RNA in water is a key challenge that must be resolved to explain the origin of protein biosynthesis.
So far, there have been no chemical methods to effectively and selectively aminoacylate RNA-2′,3′-diols with the breadth of proteinogenic amino acids in water.
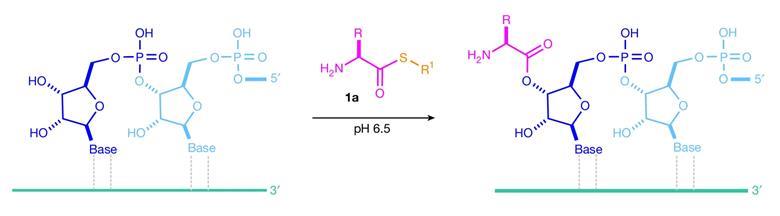
Here we demonstrate that (biological) aminoacyl-thiols (1) react selectively with RNA diols over amine nucleophiles, promoting aminoacylation over adventitious (non-coded) peptide bond formation.
Broad side-chain scope is demonstrated, including Ala, Arg, Asp, Glu, Gln, Gly, His, Leu, Lys, Met, Phe, Pro, Ser and Val, and Arg aminoacylation is enhanced by unprecedented side-chain nucleophilic catalysis.
Duplex formation directs chemoselective 2′,3′-aminoacylation of RNA.
We demonstrate that prebiotic nitriles, N-carboxyanhydrides and amino acid anhydrides, as well as biological aminoacyl-adenylates, all react with thiols (including coenzymes A and M) to selectively yield aminoacyl-thiols (1) in water. Finally, we demonstrate that the switch from thioester to thioacid activation inverts diol/amine selectivity, promoting peptide synthesis in excellent yield. Two-step, one-pot, chemically controlled formation of peptidyl-RNA is observed in water at neutral pH. Our results indicate an important role for thiol cofactors in RNA aminoacylation before the evolution of proteinaceous synthetase enzymes."
[T]eam has shown that aminoacyl–thiols are sufficiently reactive to load amino acid units onto RNA molecules without the help of enzymes
No comments:
Post a Comment